Beryl Projected Path Analysis
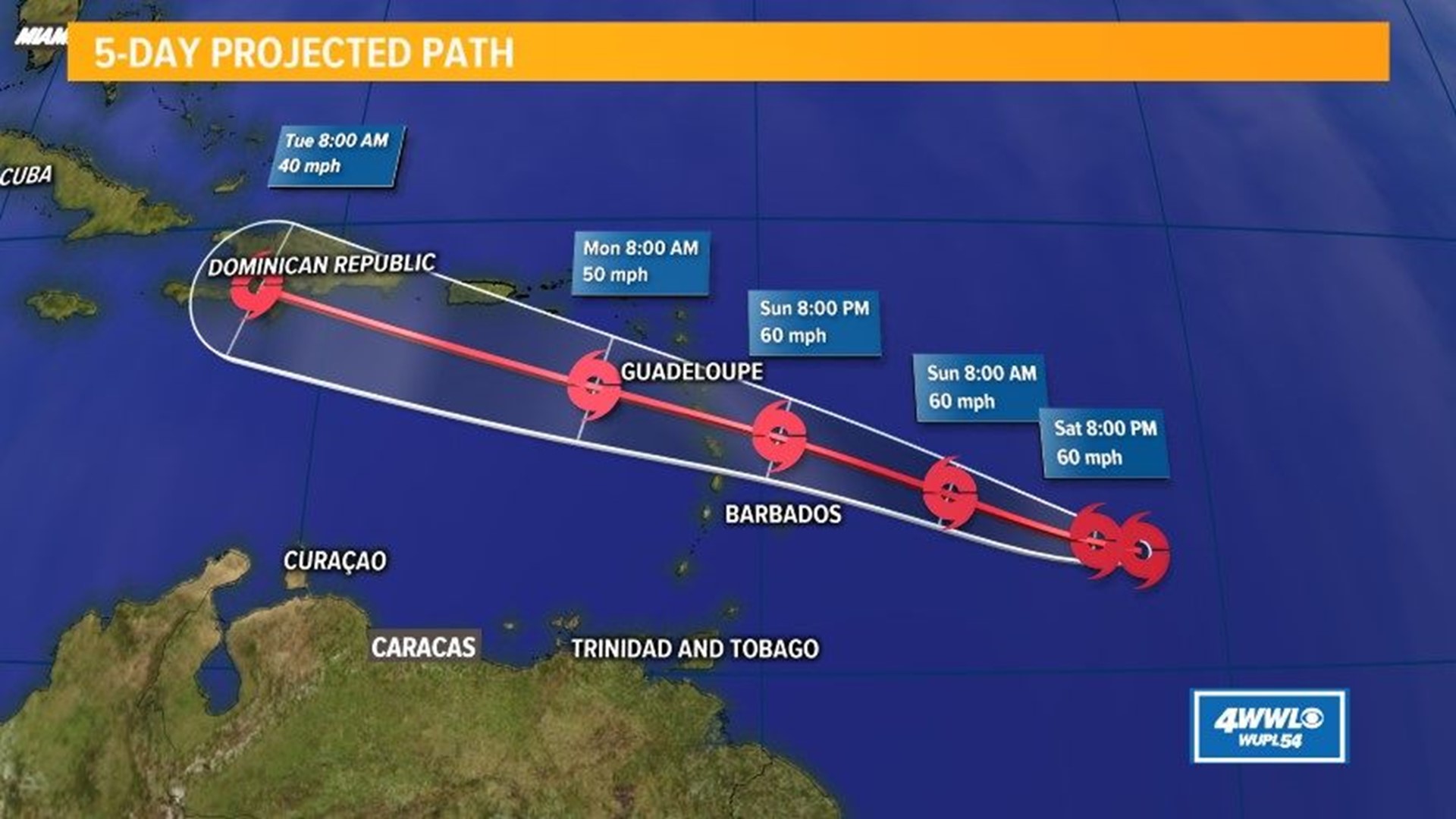
Beryl projected path – Tropical Storm Beryl is expected to continue moving west-northwestward over the next few days. The storm is currently located about 100 miles east-southeast of Jacksonville, Florida, and is moving at 12 mph. Beryl is expected to make landfall along the Florida coast on Tuesday evening or early Wednesday morning.
The projected path of Beryl, the latest tropical storm to form in the Atlantic, is expected to take it towards the Lesser Antilles by the end of the week. For the most up-to-date hurricane beryl forecast , please refer to the National Hurricane Center’s website.
The storm is expected to strengthen into a hurricane as it approaches the Caribbean Sea.
The projected path of Beryl could bring heavy rainfall, flooding, storm surge, and wind damage to the Florida coast. The storm is expected to produce rainfall totals of 4 to 8 inches, with isolated amounts of up to 12 inches possible. Storm surge could reach 4 to 6 feet along the coast, and winds could gust up to 70 mph.
The projected path of Beryl could change depending on several factors, including changes in wind direction and speed. If the storm turns more to the north, it could bring less rain and wind to the Florida coast. However, if the storm turns more to the south, it could bring more rain and wind to the area.
Beryl de projected path ah go deh shift small small, so na make dem create spaghetti models for beryl wey go show how de path fit change. Dis spaghetti models go help we know where Beryl fit land make we fit prepare well well.
Potential Impacts
The projected path of Beryl could have several potential impacts on the Florida coast, including:
- Flooding: The storm is expected to produce heavy rainfall, which could lead to flooding in low-lying areas. Flooding can damage homes and businesses, and it can also make it difficult to travel.
- Storm surge: The storm is expected to produce a storm surge of 4 to 6 feet along the coast. Storm surge can cause significant damage to coastal property, and it can also be deadly.
- Wind damage: The storm is expected to produce winds of up to 70 mph. High winds can damage trees, power lines, and buildings.
Factors Influencing Projected Path
The projected path of Beryl could be influenced by several factors, including:
- Wind direction: The direction of the wind can influence the direction of the storm. If the wind turns more to the north, the storm could turn more to the north. If the wind turns more to the south, the storm could turn more to the south.
- Wind speed: The speed of the wind can influence the speed of the storm. If the wind speed increases, the storm could move faster. If the wind speed decreases, the storm could move slower.
Beryl’s Impact on Infrastructure
As Hurricane Beryl approaches landfall, it is important to consider its potential impact on infrastructure. The storm’s strong winds and heavy rainfall could cause significant damage to roads, bridges, power lines, and other critical infrastructure.
One of the most vulnerable types of infrastructure to hurricane damage is roads. High winds can cause trees and other debris to fall onto roads, blocking them and making them impassable. Flooding can also wash out roads, creating sinkholes and making them dangerous to drive on.
Bridges are also vulnerable to hurricane damage. Strong winds can cause bridges to collapse, and flooding can scour away the foundations of bridges, making them unstable. This can disrupt transportation and make it difficult for people to get to work, school, and other important destinations.
Power lines are another type of infrastructure that is vulnerable to hurricane damage. High winds can cause power lines to snap, and flooding can cause them to short-circuit. This can lead to widespread power outages, which can disrupt businesses, schools, and homes.
Critical Infrastructure, Beryl projected path
In addition to roads, bridges, and power lines, there are other types of critical infrastructure that could be vulnerable to damage from Hurricane Beryl. These include:
- Hospitals
- Schools
- Police and fire stations
- Water treatment plants
- Communication towers
Damage to these types of infrastructure could have a significant impact on the community. For example, if a hospital is damaged, it could make it difficult for people to get the medical care they need. If a school is damaged, it could disrupt children’s education. And if a communication tower is damaged, it could make it difficult for people to stay connected with each other and with emergency responders.
Recommendations for Protecting Infrastructure
There are a number of things that can be done to protect infrastructure from the impacts of Hurricane Beryl. These include:
- Trimming trees and other vegetation around roads and bridges
- Inspecting bridges and other infrastructure for damage and making repairs as needed
- Raising the elevation of power lines
- Installing backup generators at critical facilities
- Developing evacuation plans for critical infrastructure
By taking these steps, we can help to protect our infrastructure from the impacts of Hurricane Beryl and ensure that our community is safe and resilient.
Beryl’s Impact on Coastal Communities
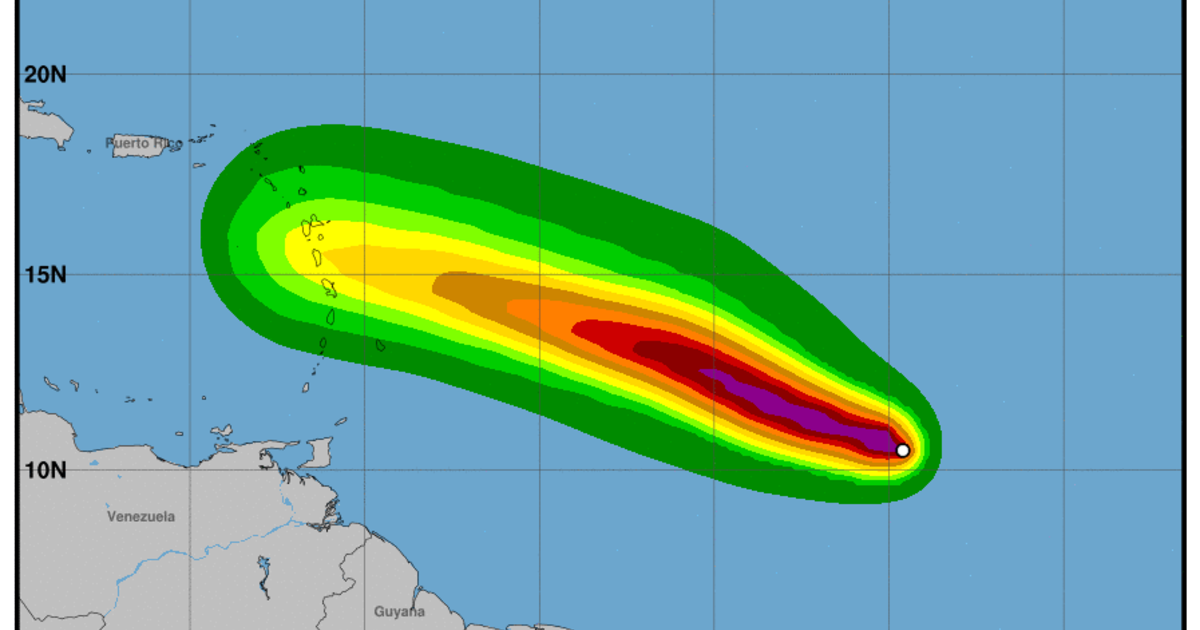
Beryl’s projected path poses significant threats to coastal communities along its trajectory. The storm’s strong winds, heavy rainfall, and potential storm surge could cause extensive damage to infrastructure, homes, and businesses.
Vulnerable coastal communities at risk from Beryl include those with low-lying areas, weak infrastructure, and a history of flooding or storm surge. These communities may experience severe flooding, erosion, and property damage.
Protecting Coastal Communities
To protect coastal communities from the impacts of Beryl, it is crucial to take proactive measures. These include:
- Strengthening infrastructure, such as seawalls, levees, and drainage systems.
- Implementing building codes that require structures to withstand high winds and flooding.
- Establishing evacuation plans and providing shelters for residents in at-risk areas.
- Educating residents about storm preparedness and response.